Geothermal energy is a renewable source of power that harnesses the heat from the Earth’s core to produce electricity. It is a clean and sustainable form of energy that has the potential to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding how geothermal energy works is key to unlocking its full potential.
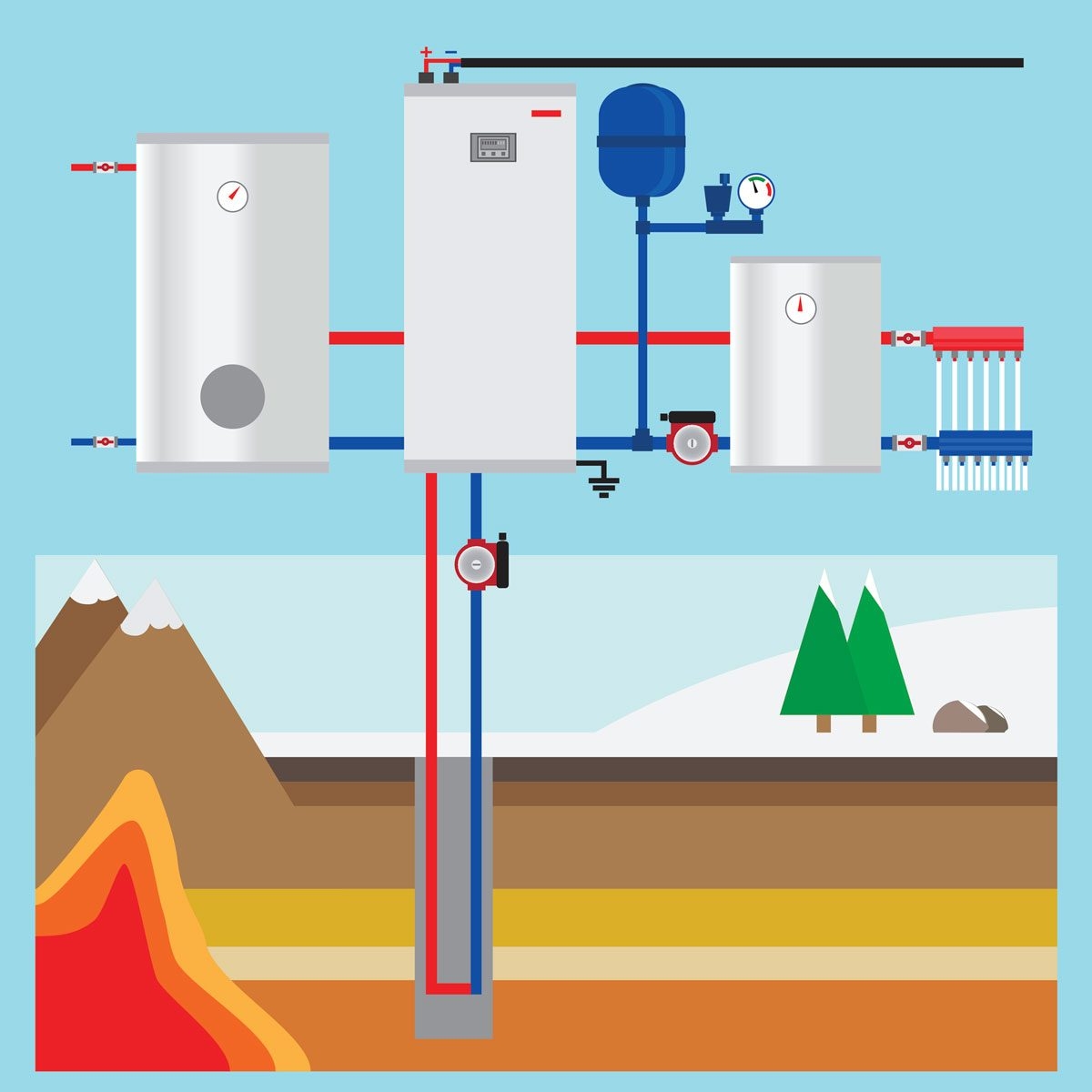
Geothermal power plants extract heat from the Earth’s core through a process that involves drilling deep into the ground to access hot water and steam. This heat is then used to drive turbines, which generate electricity. The diagram below illustrates the basic principles of how geothermal energy works.
Diagram of How Geothermal Energy Works
1. Heat Source: The Earth’s core produces heat through the decay of radioactive materials. This heat is transferred to the Earth’s crust and can be accessed through geothermal reservoirs.
2. Drilling: Geothermal power plants drill deep into the ground to access hot water and steam trapped in underground reservoirs. This hot water and steam are then brought to the surface through production wells.
3. Turbines: The hot water and steam are used to drive turbines, which are connected to generators that produce electricity. The electricity generated is then sent to the grid for distribution to consumers.
4. Re-injection: After the heat is extracted from the hot water and steam, the cooled water is re-injected back into the geothermal reservoir to maintain pressure and sustainability of the resource.
5. Environmental Benefits: Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable source of power that produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions. It also has a small land footprint compared to other forms of renewable energy.
In conclusion, geothermal energy offers a promising solution to our energy needs while reducing our impact on the environment. By understanding how geothermal energy works and utilizing its potential, we can move towards a more sustainable future for generations to come.