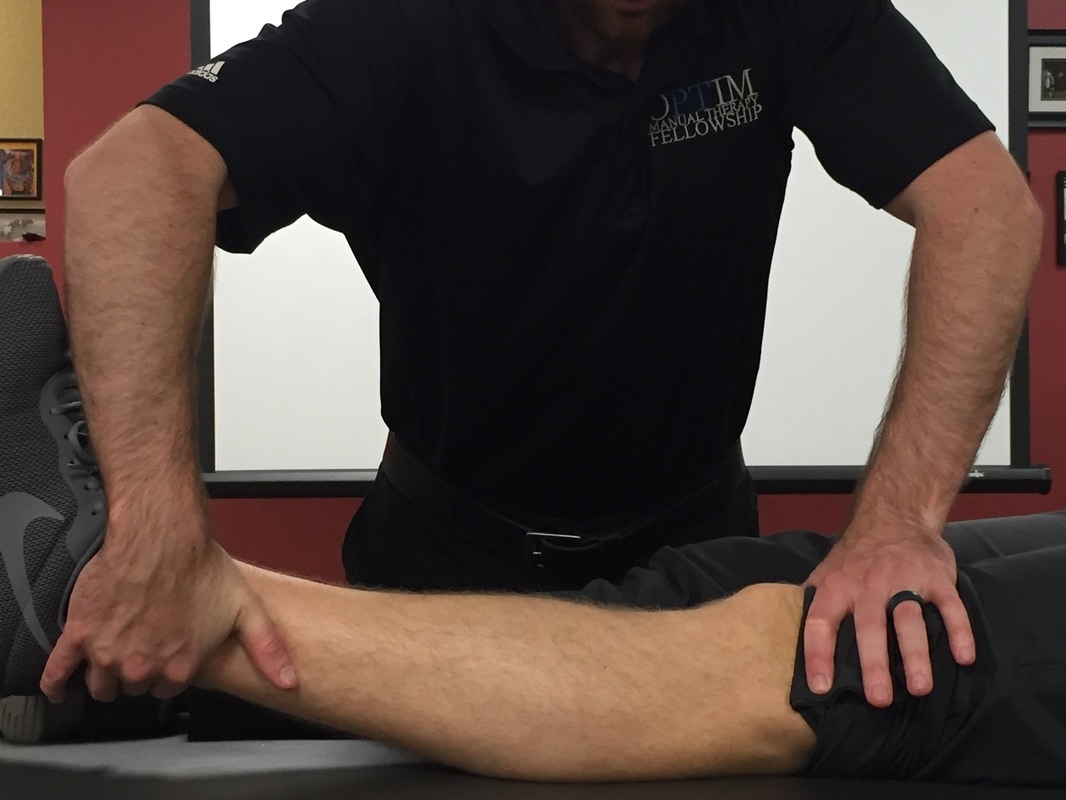
In the world of sports medicine, one of the most common tests used to diagnose knee injuries is the posterior drawer test. This test is used to assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), one of the four major ligaments in the knee. The PCL is located deep within the knee joint and plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee during movement.
During the posterior drawer test, the patient lies on their back with their knee flexed at a 90-degree angle. The examiner then places one hand on the tibia and the other hand on the femur, and gently pulls the tibia forward. If the tibia moves too far forward in relation to the femur, it may indicate a PCL injury.
Posterior Drawer Test
When performing the posterior drawer test, it is important for the examiner to have a good understanding of the anatomy of the knee joint and the mechanics of the PCL. The test should be done gently and with caution to avoid causing any further damage to the knee. The examiner should also compare the results of the test to the opposite, uninjured knee to assess for any differences in laxity.
One of the key indicators of a positive posterior drawer test is the presence of a “soft” or “mushy” endpoint when the tibia is pulled forward. This can indicate that the PCL is not providing adequate stability to the knee joint. In some cases, the patient may also experience pain or discomfort during the test, which can further support a diagnosis of a PCL injury.
In addition to assessing for laxity and pain, the examiner may also perform other tests to further evaluate the integrity of the PCL, such as the posterior sag test or the quadriceps active test. These tests can help to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the knee joint and aid in determining the appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
In conclusion, the posterior drawer test is a valuable tool in the diagnosis of PCL injuries and other knee conditions. By understanding the mechanics of the test and interpreting the results accurately, healthcare providers can effectively assess and treat patients with knee injuries. If you suspect a PCL injury, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further damage and promote optimal recovery.